Internship Course Resources for Faculty
Resources and answers to frequently asked questions (and the answers to questions you might not have known to ask) related to Internship course creation, development, and support.
To help ensure accurate tracking of URI Experiential Learning offerings and adherence to University and federal policies, connect with the CCEE (Sarah Miller) or your College/Department Experiential Office or Coordinator when you add or are considering adding an experiential component to a course.
Internships are defined by the National Association of Colleges and Employers (NACE) as: “a form of experiential learning that integrates knowledge and theory learned in the classroom with practical application and skills development in a professional setting. Internships give students the opportunity to gain valuable applied, authentic experience and make connections in professional fields they are considering for career paths; and give employers the opportunity to guide and evaluate talent.” In addition, an internship is a semester (fall, spring, summer) in duration, may or may not carry credit, may be paid or unpaid based on the Department of Labor criteria.
Internship Course Best Practices:
- Incorporate essential assignments and evaluations (see sample syllabi below for ideas)
- Confirm site and supervision support
- Ensure hours align with credits earned
- Review important logistical processes related to agreements, risk, and transportation
- Integrate critical reflection activities and assignments
- Incorporate resources to draw a connection between your class content and industry
Review each item (see tabs below) to ensure a successful internship experience.
National Council for State Authorization Reciprocity Agreements (NC-SARA)
The National Council for State Authorization Reciprocity Agreements (NC-SARA) establishes comparable national standards for interstate offering of postsecondary distance-education courses and programs. As part of the University’s membership in NC-SARA, we are required to collect basic placement site information from students enrolled in Internship courses. As such, students enrolled in Internship courses receive an e-campus to-do request titled “Internship Site Information,” and we ask for your assistance in reminding your students to complete this request. Questions can be sent to Sarah Miller at sgmiller@uri.edu.
Most Requested Information
Site & Supervision
- Supervision is a required and critical component to an internship now only because it ensures a quality and high impact experience for your student and employer, but supervison is required for legal and insurance coverage.
- In order to sustain clear and consistent communication, you should utilize various methods including Site Supervisor contact sheets, pre and post surveys, check-ins, and site visits. At minimum we recommend an initial introduction and a final evaluations, but your course experience (or site partners) might require additional contact points.
- Sample ITR Internship Program information for employers
- Resources for creating internships at URI
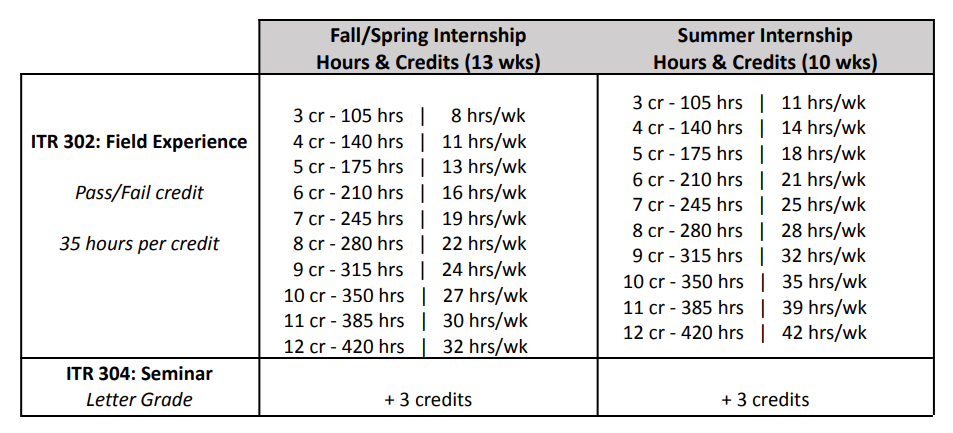
Hours per Credit
CCEE recommends the following hours per credit breakdown, as shown in the ITR Internship Program:
Affiliation Agreements
When engaging with industry and community partners through experiential education, agreements and memorandums of understanding (MOU) are often entered into to support and outline the terms of the engagement. The URI Office of the General Counsel (OGC) is responsible for the coordination and management of all legal issues affecting the University including agreements and MOU’s.
- Not all internship sites will require or need an agreement or Memorandum of Understanding. Most sites will notify you or the student if this is a needed. If so, follow the suggestions below.
- If you receive an agreement for a student internship or field experience site that requires a signature from URI, do not sign.
- Review the OGC website including the New Matter Onboarding Protocol and Contract Review Protocol.
- An agreement or contract signed by an unauthorized individual will not be considered binding on the University of Rhode Island. It will be considered to be a personal agreement or contract binding on the person who signed it.
- CCEE, in partnership with URI OGC, has created an individual student intern agreement template that can be used when individual agreements are needed but the site does not have one.
- Please contact URI General Counsel at 874-4486 or OGC_Service_Request@etal.uri.edu with questions regarding agreements and contracts.
Other Internship Resources
Students at URI can gain experience in an internship through their academic department or through the CCEE ITR Internship Program at the Center for Career and Experiential Learning.
- For detailed information on how to create an internship description or the types of engagement available to you please view the Employer Guide to Creating a Meaningful Learning Experience which is made possible by a collaboration of RI colleges, universities, and institutions of higher education in an effort to support our students and our employer partners.
- For guidance on how to adjust an internship to reflect the shift to virtual work we have created this guide to Creating Virtual Internships at URI .
- Information on funding support for employers offering internships can be found on the website for the Governor’s Workforce Board, including the Work Immersion Training Grants. Work Immersion Training Grants offer up to 50% wage reimbursements to any RI business that provides a temporary paid work experience to Rhode Island college students, RI Career and Technical Education high school students and unemployed adults.
- Information specific to the ITR Internship Program, including requirements and paperwork can be found here.
- NACE Internship Principles regarding unpaid internships provide guidance
- Fair Labor Standards Act outlined by The US Department of Labor
Internship Tips for Advisors
Consider the following when assisting students to find an appropriate internship or experiential opportunity to meet their current learning goals:
- Understand the types of experiential education opportunities available
- Does the student have elective credit available for an internship or other experiential course?
- If the student can enroll in an Internship course, what type of course would best fit? Some Internship courses are highly structured, like the ITR Internship Program, which means the student will have significant guidance and support throughout the entire experience. Other Internship courses might be more “low-touch” courses and provide pass/fail credit (no seminar) with minimal professional career reflection and touchpoints.
Sample Internship Course Syllabi
| Subject | Catalog | Course Title | Method of Instruction | Grading Scheme | Syllabus Link | Experiential Education Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSV | 303 | Off-Campus Community Service | Practicum/Online | S/U | CSV 303 Syllabus Sample | Service-Learning |
| ITR | 302 | Field Experience | Practicum/Online | S/U | ITR 302 Field Experience | Internship |
| ITR | 302 | Non Seminar Field Experience | Practicum/Online | S/U | ITR 302 Non Seminar | Internship |
| ITR | 304 | Internship Seminar | Seminar/Online | Letter Grade | ITR 304 Internship Seminar | NA |
| SAMPLE | TEMPLATE | Field Experience/ Internship | Practicum | S/U | Syllabus Sample | NA |
| CSC | 477 | Computer Science Internship | Practicum | Letter Grade | CSC 477 Computer Science Internship | Internship |
