Current Area Research
- Determining the Role of the Fanconi Anemia Pathway in the Suppression of Structural Variation - Copy number variation (CNV) refers to genomic deletions or duplications of tens of thousands to millions of nucleotides. CNV is both a normal feature of genetic variation and a major contributor to genetic disease, e.g., neurological disease and cancer. The mechanisms by which CNVs arise and the cellular pathways that suppress CNV formation are largely […]
 Fanconi Anemia and MiDAS: - Several FA proteins have been functionally linked to the process of mitotic DNA synthesis, also known as MiDAS. While the bulk of DNA synthesis occurs during S-phase, under conditions of replication stress, e.g., following treatment with aphidicolin (APH), DNA synthesis can still be observed during prophase/prometaphase. This mitotic DNA synthesis process is thought to be […]
Fanconi Anemia and MiDAS: - Several FA proteins have been functionally linked to the process of mitotic DNA synthesis, also known as MiDAS. While the bulk of DNA synthesis occurs during S-phase, under conditions of replication stress, e.g., following treatment with aphidicolin (APH), DNA synthesis can still be observed during prophase/prometaphase. This mitotic DNA synthesis process is thought to be […]- Fanconi Anemia, Retinoic Acid Signaling, and Retinaldehyde Genotoxicity - FA patients frequently exhibit heterogeneous and multisystemic congenital abnormalities. Patients from certain FA complementation groups are also at increased risk for embryonal tumors. These observations suggest defects in a key developmental biology pathway in FA and the existence of a FA-specific teratogen and embryonal mutagen. In recent RNA-seq studies, we have discovered dysregulation of retinoic […]
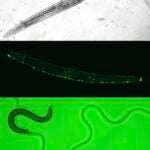 A C. elegans Model of Fanconi Anemia Neurological Syndrome (FANS) - Although FA is primarily characterized by increased risk for bone marrow failure and cancer, several recent clinical reports describe pleiotropic neurological symptoms in FA patients, including abnormal brain MRIs, seizures, brain lesions, and early-onset cognitive decline. This constellation of neurological symptoms is collectively referred to as Fanconi Anemia Neurological Syndrome (FANS). The molecular etiology of […]
A C. elegans Model of Fanconi Anemia Neurological Syndrome (FANS) - Although FA is primarily characterized by increased risk for bone marrow failure and cancer, several recent clinical reports describe pleiotropic neurological symptoms in FA patients, including abnormal brain MRIs, seizures, brain lesions, and early-onset cognitive decline. This constellation of neurological symptoms is collectively referred to as Fanconi Anemia Neurological Syndrome (FANS). The molecular etiology of […]
Bibliography
1. Arlt, M.F., Mulle, J.G., Schaibley, V.M., Ragland, R.L., Durkin, S.G., Warren, S.T., and Glover, T.W. (2009). Replication stress induces genome-wide copy number changes in human cells that resemble polymorphic and pathogenic variants. Am J Hum Genet 84, 339-350.
2. Arlt, M.F., Wilson, T.E., and Glover, T.W. (2012). Replication stress and mechanisms of CNV formation. Curr Opin Genet Dev 22, 204-210.
3. Bhowmick, R., Minocherhomji, S., and Hickson, I.D. (2016). RAD52 facilitates mitotic DNA synthesis following replication stress. Mol Cell 64, 1117-1126.
4. Garribba, L., Wu, W., Özer, Ö., Bhowmick, R., Hickson, I.D., and Liu, Y. (2018). Inducing and Detecting Mitotic DNA Synthesis at Difficult-to-Replicate Loci. Methods Enzymol 601, 45-58.
5. Graber-Feesl, C.L., Pederson, K.D., Aney, K.J., and Shima, N. (2019). Mitotic DNA synthesis is differentially regulated between cancer and noncancerous cells. Mol Cancer Res : MCR 17, 1687-1698.
6. Howlett, N.G., Taniguchi, T., Durkin, S.G., D’Andrea, A.D., and Glover, T.W. (2005). The Fanconi anemia pathway is required for the DNA replication stress response and for the regulation of common fragile site stability. Hum Mol Genet 14, 693-701.
7. Kottemann, M.C., and Smogorzewska, A. (2013). Fanconi anaemia and the repair of Watson and Crick DNA crosslinks. Nature 493, 356-363.
8. Madireddy, A., Kosiyatrakul, S.T., Boisvert, R.A., Herrera-Moyano, E., Garcia-Rubio, M.L., Gerhardt, J., Vuono, E.A., Owen, N., Yan, Z., Olson, S., et al. (2016). FANCD2 facilitates replication through common fragile sites. Mol Cell 64, 388-404.
9. Okamoto, Y., Iwasaki, W.M., Kugou, K., Takahashi, K.K., Oda, A., Sato, K., Kobayashi, W., Kawai, H., Sakasai, R., Takaori-Kondo, A., et al. (2018). Replication stress induces accumulation of FANCD2 at central region of large fragile genes. Nucleic Acids Res 46, 2932-2944.
10. Schlacher, K., Wu, H., and Jasin, M. (2012). A distinct replication fork protection pathway connects Fanconi anemia tumor suppressors to RAD51-BRCA1/2. Cancer Cell 22, 106-116.
11. Wilson, T.E., Arlt, M.F., Park, S.H., Rajendran, S., Paulsen, M., Ljungman, M., and Glover, T.W. (2015). Large transcription units unify copy number variants and common fragile sites arising under replication stress. Genome Res 25, 189-200.
