Demonstrations, Seminars, and Workshops
Instrumentation Update
Instruments in Action
Demonstrations, Seminars, and Workshops
The Centralized Research Core Facility (CRCF) hosted a Leica Microsystems workshop featuring THUNDER imaging and Aivia artificial intelligence (AI) analysis. Leica THUNDER, an imaging technology, is designed to  improve the optical resolution of microscopy images. THUNDER uses computational methods to reconstruct high-resolution images from the acquired data, providing clearer and more detailed images compared to traditional microscopy techniques. Aivia, an advanced image analysis software, incorporates AI algorithms to automate the analysis of complex biological images acquired through microscopy. Aivia can be used for tasks such as cell counting, object recognition, and tracking in time-lapse experiments.
improve the optical resolution of microscopy images. THUNDER uses computational methods to reconstruct high-resolution images from the acquired data, providing clearer and more detailed images compared to traditional microscopy techniques. Aivia, an advanced image analysis software, incorporates AI algorithms to automate the analysis of complex biological images acquired through microscopy. Aivia can be used for tasks such as cell counting, object recognition, and tracking in time-lapse experiments.  During the two-week workshop, more than thirteen researchers from URI departments of Biology, Pharmacy, Physics, and Engineering had the opportunity to image and analyze their samples.
During the two-week workshop, more than thirteen researchers from URI departments of Biology, Pharmacy, Physics, and Engineering had the opportunity to image and analyze their samples.
Top
Instrumentation Update
The CRCF purchased two new instruments: the NanoTemper Monolith X and the BioTek Synergy H1 Multimode Reader. To accommodate the demands and needs of researchers statewide, the CRCF applied for the National Institutes of Health (NIH) supplemental funds PA-20-272 grant to acquire the NanoTemper Monolith X instrument. The NanoTemper Monolith X, a fluorescence-based detection system, accurately assesses biomolecular interactions using MicroScale Thermophoresis (MST). The Monolith X complements the CRCF’s existing Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) technology by combining isothermal spectral shift measurement with MST technology, further enhancing the CRCF capabilities in molecular interaction analysis.
instrument. The NanoTemper Monolith X, a fluorescence-based detection system, accurately assesses biomolecular interactions using MicroScale Thermophoresis (MST). The Monolith X complements the CRCF’s existing Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) technology by combining isothermal spectral shift measurement with MST technology, further enhancing the CRCF capabilities in molecular interaction analysis.

In January 2024, the BioTek Synergy H1 replaced the CRCF’s existing SpectraMax readers. The BioTek Synergy H1 Multimode Reader, a cutting-edge modular multimode microplate reader, is capable of performing absorbance, fluorescence, and luminescence readings. This state-of-the-art instrument is a valuable asset for supporting all research and academic pursuits at URI, all nine participating RI-INBRE research institutions, and RI’s biomedical research community.
Top
Instruments in Action
Fang Wang (RI-INBRE investigator, SURF mentor, and Assistant Professor in the URI Chemistry Department) published two notable papers on protein and peptide synthetic modification attaining crucial data which included high-resolution mass spectra and MS/MS analyses, using the AB SCIEX TripleTOF 4600 mass spectrometer equipped with a DuoSpray™ ion source instrument located in the CRCF and facilitated by the CRCF.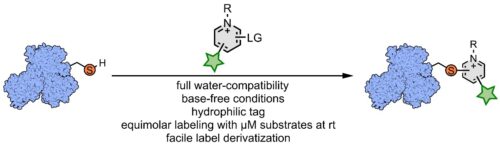 The first paper was featured in “Bioconjugate Chemistry” and the second paper published in the “Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS).” These two papers highlight a novel strategy distinctive from conventional cysteine bioconjugation methods. Using highly reactive and hydrophilic pyridinium salts, quantitative cysteine bioconjugation can be achieved at low micromolar concentrations under fully biocompatible conditions. The versatility of this chemistry is underscored by its ability to accommodate various functionalities and synthetic handles useful for chemical biology without a significant loss in reactivity. Overall, the authors anticipate this chemistry to be a practical and user-friendly addition to the chemical biology toolbox.
The first paper was featured in “Bioconjugate Chemistry” and the second paper published in the “Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS).” These two papers highlight a novel strategy distinctive from conventional cysteine bioconjugation methods. Using highly reactive and hydrophilic pyridinium salts, quantitative cysteine bioconjugation can be achieved at low micromolar concentrations under fully biocompatible conditions. The versatility of this chemistry is underscored by its ability to accommodate various functionalities and synthetic handles useful for chemical biology without a significant loss in reactivity. Overall, the authors anticipate this chemistry to be a practical and user-friendly addition to the chemical biology toolbox.
Top
