Seamless Co-Simulation: Bridging Cyber and Physical Domains
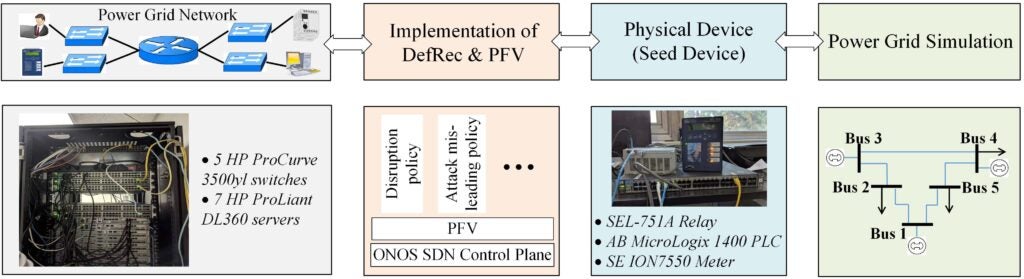
Building a representative cyber-physical testbed requires mirroring real power-grid operations by seamlessly linking physical electronic hardware, communication-network devices, and power-system simulators—while still remaining scalable, repeatable, and cost-effective in a laboratory setting. Manually integrating disparate simulators can be both prohibitive and error-prone.
To overcome these challenges, we have explored several advanced tools and methodologies for realistic cyber-physical co-simulation in our evaluation testbed:
- Network Deployment Strategies: We compared three approaches—Mininet emulation, GENI shared-cloud environments, and VLAN-based hardware switches—to balance realism, scalability, and repeatability.
- Modular Testbed Architecture: We designed a plug-and-play framework that integrates real intelligent electronic devices (IEDs) such as the SEL-751A, AB MicroLogix 1400, and SE ION 7550, alongside SDN controllers and power-grid simulators.
- HELICSAuto: We developed HELICSAuto, a syntax-driven instrumentation tool that automatically wraps domain simulators (PandaPower, PowerWorld, OPAL-RT, PyDNP3) with HELICS APIs—dramatically cutting manual effort and ensuring robust co-simulation federation.
