1. Understand the Cp-Time profile observed from multiple oral doses, with special emphasis on steady state 2. Appreciate the impact of the rate and extent of absorption on the Cp-time profile 3. Appreciate how the relationship between tau and t1/2 influences fluctuation
Continue reading "Multiple Oral Doses (Chapter 14)"Author: Ian T Lester
Nonlinear Pharmacokinetics (Chapter 15)
1. Using phenytoin as an example, understand a model for capacity limited elimination 2. Observe how increases in the rate of administration affect Cp 3. Understand how Vmax and Km influence the Cp-Time profile
Continue reading "Nonlinear Pharmacokinetics (Chapter 15)"Sigmoidal Emax Model (Chapter 16)
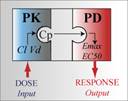
1. Introduce the characteristics of the Sigmoidal Emax and Emax models 2. Compare the time course of Cp and Response after a dose 3. Illustrate how pharmacodynamics can influence a drug’s duration of action 4. Illustrate the impact of the slope or sigmoidicty factor ‘n’
Continue reading "Sigmoidal Emax Model (Chapter 16)"Sigmoidal Emax Model With an Effect Compartment (Chapter 16)
1. Demonstrate how an effect compartment can be linked to a PK and PD model 2. Illustrate hysteresis 3. Illustrate the importance of keo
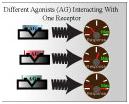
Continue reading "Sigmoidal Emax Model With an Effect Compartment (Chapter 16)"Operational Model of Agonism (Chapter 17)
1. Observe how the OMA can be used to assess drug efficacy in-vivo. 2. Observe how a drug’s efficacy in a system depends on the concentration of working receptors in the system. 3. Observe how the transduction ratio can be used to assess efficacy.
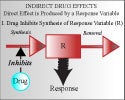
Continue reading "Operational Model of Agonism (Chapter 17)"Indirect Effect Model I: Inhibition in kin (Chapter 17)
1. Understand the structure of the indirect model 2. Understand the influence of model parameters on response 3. Appreciate the factors that control the onset magnitude and duration of response
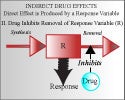
Continue reading "Indirect Effect Model I: Inhibition in kin (Chapter 17)"Indirect Effect Model II: Inhibition of kout (Chapter 17)
1. Understand the structure of the indirect model 2. Understand the influence of model parameters on response 3. Appreciate the factors that control the onset magnitude and duration of response
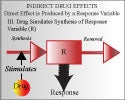
Continue reading "Indirect Effect Model II: Inhibition of kout (Chapter 17)"Indirect Effect Model III: Stimulation of kin (Chapter 17)
1. Understand the structure of the indirect model 2. Understand the influence of model parameters on response 3. Appreciate the factors that control the onset magnitude and duration of response
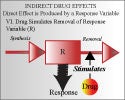
Continue reading "Indirect Effect Model III: Stimulation of kin (Chapter 17)"Indirect Effect Model IV: Stimulation of kout (Cchapter 17)
1. Understand the structure of the indirect model 2. Understand the influence of model parameters on response 3. Appreciate the factors that control the onset magnitude and duration of response
Continue reading "Indirect Effect Model IV: Stimulation of kout (Cchapter 17)"Transit Compartment (Chapter 17)
1. Understand the characteristics of the transit compartment model 2. Observe how the response profile changes between compartments 3. Observe how the response is influenced by the dose 4. Observe how the response is influenced by the number of compartments and by the total mean transit time
Continue reading "Transit Compartment (Chapter 17)"