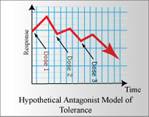
1. Use the model for nicotine’s effect on heart rate to demonstrate how tolerance can be modeled using a hypothetical metabolite that acts as a drug antagonist 2. Observe how the model can be used to understand the time course of tolerance and to plan compensatory strategies to minimize drug tolerance
Continue reading "Hypothetical Antagonist Model For Tolerance (Chapter 17)"Author: Ian T Lester
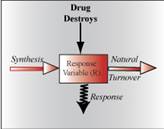
Precursor Pool Depletion Model For Tolerance (Chapter 17)
Hematological Toxicity of Anticancer Drugs (Chapter 17)
1. Present the structure of a PD model for the hematological toxicty 2. Observe the onset, duration of, and recovery from, drug-induced neutropenia 3. Observe how a drug’s PK and PD effects the duration and intensity of neutropenia
Continue reading "Hematological Toxicity of Anticancer Drugs (Chapter 17)"Irreversible Effects (Chapter 17)
1. Understand how irreversible drug effects can be modeled 2. Observe the time course of plasma concentrations and response 3. Using a simulation model based on disolvprazole (see text), observe how irreversible drug effects impact the design of dosing regimens
Continue reading "Irreversible Effects (Chapter 17)"