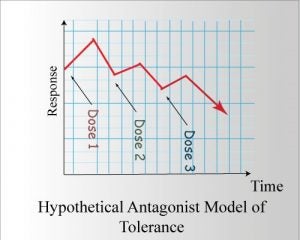
Tolerance may be defined as a process that results in a reduction in the response to a specific drug concentration following repeated drug exposure. One model for tolerance assumes that the drug produces a hypothetical metabolite that opposes its action.
Link to Model
See Chapter 20: Semimechanistic PK-PD Models
Topics relevant to this model are covered in the following sections:
– 20.6 Models of Tolerance
– 20.6.1 Introduction to Pharmacologic Tolerance
– 20.6.2 Counter-Regulatory Force Tolerance Model
– 20.6.2.1 Simulation Exercise
Basic Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics: An Integrated Textbook and Computer Simulations 2nd Edition
By: Sara E. Rosenbaum
Purchase from Amazon