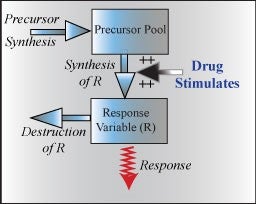
Tolerance may be defined as a process that results in a reduction in the response to a specific drug concentration following repeated drug exposure. Tolerance could occur if an endogenous compound that plays an essential role in the response chain becomes depleted during response. This model assumes the drug stimulates the production of a response variable which becomes then becomes depleted.
Link to Model
See Chapter 20: Semimechanistic PK-PD Models
Topics relevant to this model are covered in the following sections:
– 20.6 Models of Tolerance
– 20.6.1 Introduction to Pharmacologic Tolerance
– 20.6.3 Precursor Pool Model of Tolerance
– 20.6.3.1 Simulation Exercise
Basic Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics: An Integrated Textbook and Computer Simulations 2nd Edition
By: Sara E. Rosenbaum
Purchase from Amazon