See what it’s like to be a PharmD student at URI College of Pharmacy.
Continue reading "October 22, 2024 @ 1:00pm – Pharm.D. Class Shadow"Author: Ian T Lester
October 10, 2024 @ 1:00pm – Pharm.D. Class Shadow
See what it’s like to be a PharmD student at URI College of Pharmacy.
Continue reading "October 10, 2024 @ 1:00pm – Pharm.D. Class Shadow"October 3, 2024 @ 1:00pm – Pharm.D. Class Shadow
See what it’s like to be a PharmD student at URI College of Pharmacy.
Continue reading "October 3, 2024 @ 1:00pm – Pharm.D. Class Shadow"October 1, 2024 @ 1:00pm – Pharm.D. Class Shadow
See what it’s like to be a PharmD student at URI College of Pharmacy.
Continue reading "October 1, 2024 @ 1:00pm – Pharm.D. Class Shadow"November 21, 2025 @ 1:00 – 3:00pm – College of Pharmacy Exploration Day
Registration Open | In-person | PharmD | BSPS
Visit the college and participate in a range of hands on events. High school students with an interest our programs as well as family members and teachers are welcome.
Continue reading "November 21, 2025 @ 1:00 – 3:00pm – College of Pharmacy Exploration Day"Zoom BSBPS Career Panel
Registration Open | Zoom | BSPS
Join us on Zoom to hear a panel of alumni discuss their day-to-day responsibilities, what they love about their jobs, their path to their current roles, and what they wish they knew on their first day of work.
Continue reading "Zoom BSBPS Career Panel"Zoom Pharm.D. Career Panel
Registration Open | Zoom | PharmD
Join us on Zoom to hear from several alumni and current students to participate in an interactive panel discussing their role in various practice areas, insight into their path, and how their education has prepared them for the future.
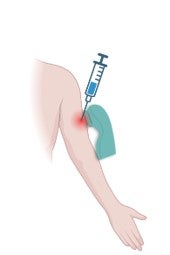
Continue reading "Zoom Pharm.D. Career Panel"Radiofrequency adjuvant
Safe and potent adjuvants are highly demanded to aid in development of new and improved vaccines. Due to the slow progress in developing novel chemical adjuvants, we took a different approach to develop physical radiofrequency adjuvant (RFA) to boost vaccination. RFA emits alternating electromagnetic fields in the skin surface and induce tissue stress to alert […]
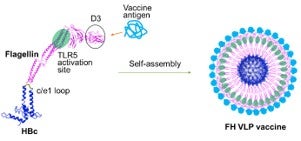
Continue reading "Radiofrequency adjuvant"High-density flagellin-displayed virus-like particle platform
Virus-like particles (VLPs) simulate natural viruses and are able to induce potent humoral and cellular immune responses. VLPs have been attractive vaccine delivery platforms due to their high immunogenicity and safety. Hepatitis b core (HBc) VLPs have been widely explored to display foreign antigens by insertion into its c/e1 loop. Yet, only small antigenic peptides […]
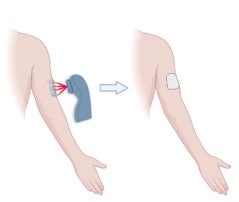
Continue reading "High-density flagellin-displayed virus-like particle platform"Laser-facilitate transdermal drug delivery and vaccination
This project explores ablative fractional laser as a minimally invasive tool to generate skin microchannels to facilitate transcutaneous drug delivery and vaccination. Various patch systems are developed to allow powder drugs to be loaded for convenient delivery via laser-generated skin microchannels. Laser-based powder delivery takes advantage of water evaporated from skin microchannels to dissolve topical […]
Continue reading "Laser-facilitate transdermal drug delivery and vaccination"